In our quest for healthy and protected skin, it is crucial to understand the radiation emitted by the sun and its impact on our epidermis. Let's dissect together the different nuances of these rays and their implications on the health of our skin
The sun emits broad spectrum radiation which includes visible light but also UV radiation. The term “ UV ” means “ ultraviolet ”. Violet is the color with the highest frequency of visible light. Ultraviolet is therefore radiation “beyond” violet which is invisible to the human eye.
UV is classified into several categories based on their wavelength. UVA extends from 315 to 400 nm, UVB between 280 and 315 nm and UVC (stopped by the ozone layer) between 100 and 280 nm.
High dose exposure to UVA and UVB is harmful to our health and our skin.
The WHO estimates that “ more than 90% of the global burden of melanoma and other skin cancers is attributable to radiation exposure
UV”. UV rays have no effect on the sensation of heat we feel in the sun which is due to infrared rays. It is important to note that UV is all around us even on cloudy or cold days !
This is why we must protect our skin from the sun at all times.
Beware of preconceived ideas : SPF 50 does not mean that the product protects you for 50 minutes!
The SPF (Sun Protection Factor) or FPS (Facteur de Protection Solaire) in French is the ratio between the minimum erythemal dose (the smallest amount of UV that triggers a sunburn) on skin protected by a sun protection product and the minimum erythemal dose on the same unprotected skin.
SPF is a ratio of time with and without sun protection before sunburn appears. In other words, it will take us 50 times longer to get sunburned with SPF50 sunscreen than without it. Note that an SPF 30 product blocks 96.7% of UVB while an SPF 50+ blocks 98.3% of UVB.
UVB = Burn = Immediate Effect
UVB represents 5% of UV and is responsible for the tan that we observe 48 hours to 72 hours after exposure . It has long been proven that they induce DNA lesions (deleterious DNA damage) and promote the appearance of skin cancers .
“ Sunburn ” is a symptom visible to the naked eye of overexposure to UVB. This is a skin burn which can be first degree (redness
without blisters), second degree (appearance of blisters)
or deep second degree (destroyed skin vessels).
UVA = Age = Long Term Effect
Historically, harmful effects were only attributed to UVB. UVA has also been shown to play an important role in DNA damage , inducing photodermatoses (abnormal condition (redness, blisters, etc.) of the skin following sun exposure) and photoimmunosuppression (the consequences pathogenic UVB radiation can be observed in the aggravation of infectious diseases and the development of skin cancer).
UVA radiation is also involved in skin aging . They represent 95% of UV rays and damage the elastin and collagen fibers of the dermis, promoting sagging of the skin and the appearance of signs of aging .
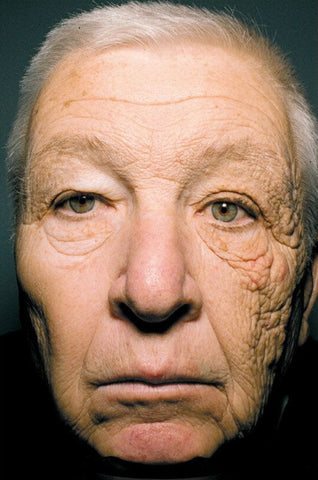
William Edward McElligott , a 59 year old American is a perfect example of this
phenomenon. The left half of his face is aged in appearance with deeper wrinkles and sagging skin. William Edward is a deliveryman and passes the
most of his day in his truck. UVA, passing through the glass , induced photoaging on the exposed part of his face.
It is therefore very important that a solar product is broad spectrum
(i.e. it protects against UVB and UVA) so that the user is sufficiently protected against the harmful effects of the entire UV spectrum of radiation
solar.
The WHO indicates that applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a protection factor of at least SPF15 is one of the safety measures that would prevent a large number of cancers caused by UV radiation.
Protecting your skin from UV rays, whether it's sunny or cloudy, is vital to preventing long-term damage. Choose broad-spectrum sun protection for complete defense against the harmful effects of the sun and adopt safe practices during your outdoor activities.
